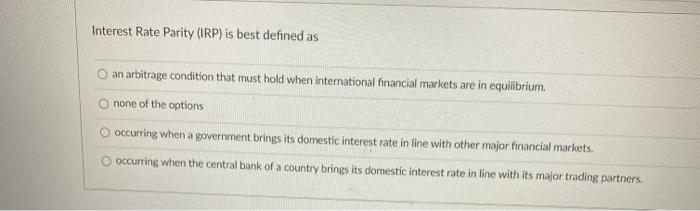
Interest Rate Parity (irp) Is Best Defined As
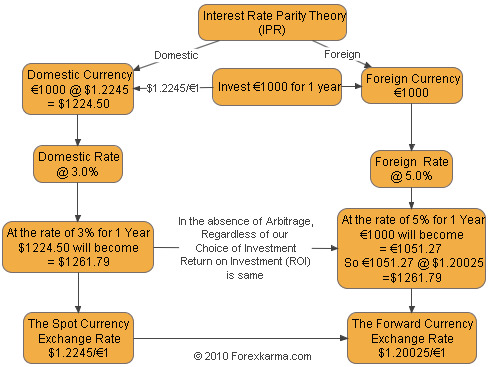
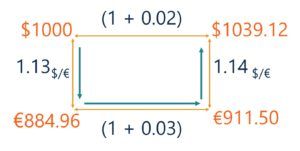
Interest rate parity (irp) is best defined as. Interest Rate Parity IRP is best defined as A. Interest rate parity IRP is a theory according to which the interest rate differential between two countries is equal to the differential between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange. The term is somewhat of a misnomer on the basis of how it is being described here as it should really be called rate of return parity.
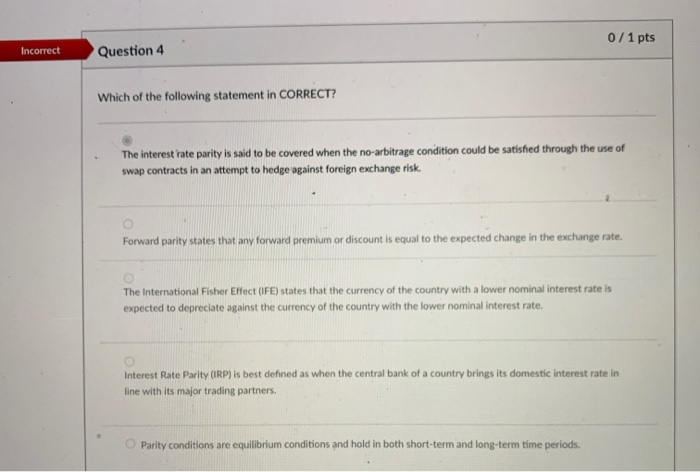
Interest Rate Parity IRP is best defined as. When the central bank of a country brings its domestic interest rate in line with its major trading partners. Uncovered interest rate parity UIP theory states that the difference in interest rates between two countries will equal the relative change in currency foreign exchange rates over the same.
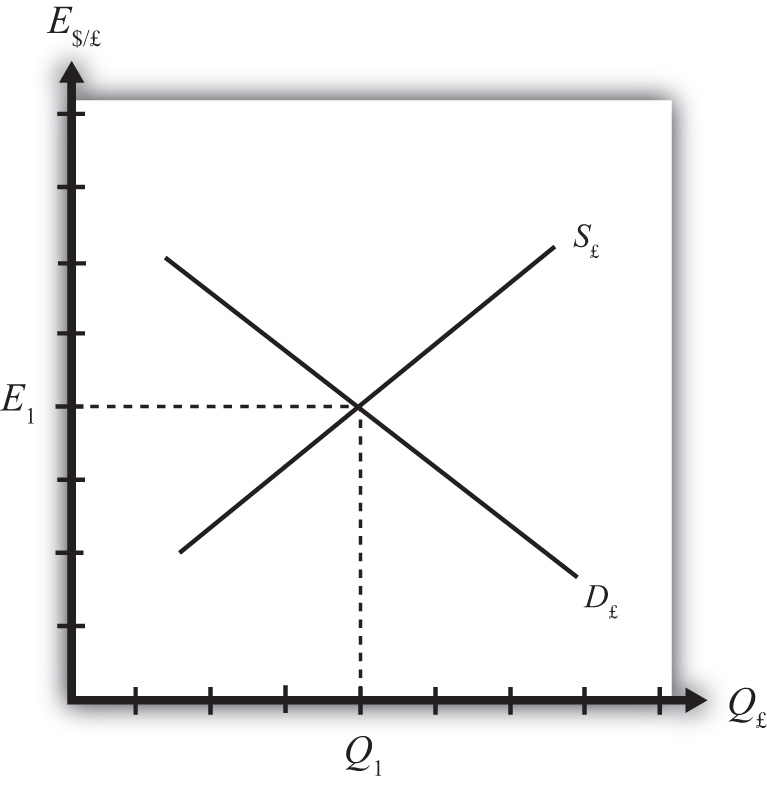
Covered interest rate parity refers to a theoretical condition in which the relationship between interest rates and the spot and forward currency values of two countries are in equilibrium. None of the options occurring when a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial markets. When a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial markets.
Interest Rate Parity IRP is best defined as. When a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial marketsB. Interest rate parity IRP is the fundamental equation that governs the relationship between interest rates and currency exchange rates.
When a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial marketsB. When Interest Rate Parity IRP does not hold. Interest rate parity refers to a condition of equality between the rates of return on comparable assets between two countries.
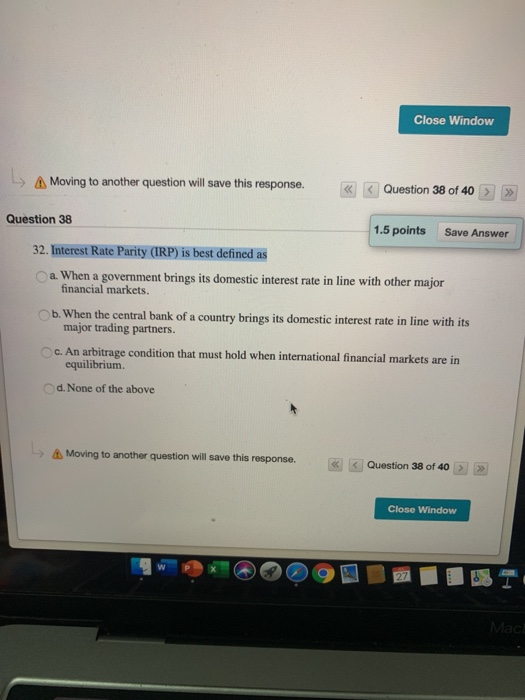
When a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial markets. Interest Rate Parity IRP is best defined as. A zero arbitrage condition that must hold when international financial markets are in equilibriumD.
Occurring when the central bank of a country brings its domestic interest rate in line with its major trading partners. When the central bank of a country brings its domestic interest rate in line with its major trading partnersC.
Interest rate parity IRP is a theory according to which the interest rate differential between two countries is equal to the differential between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange.
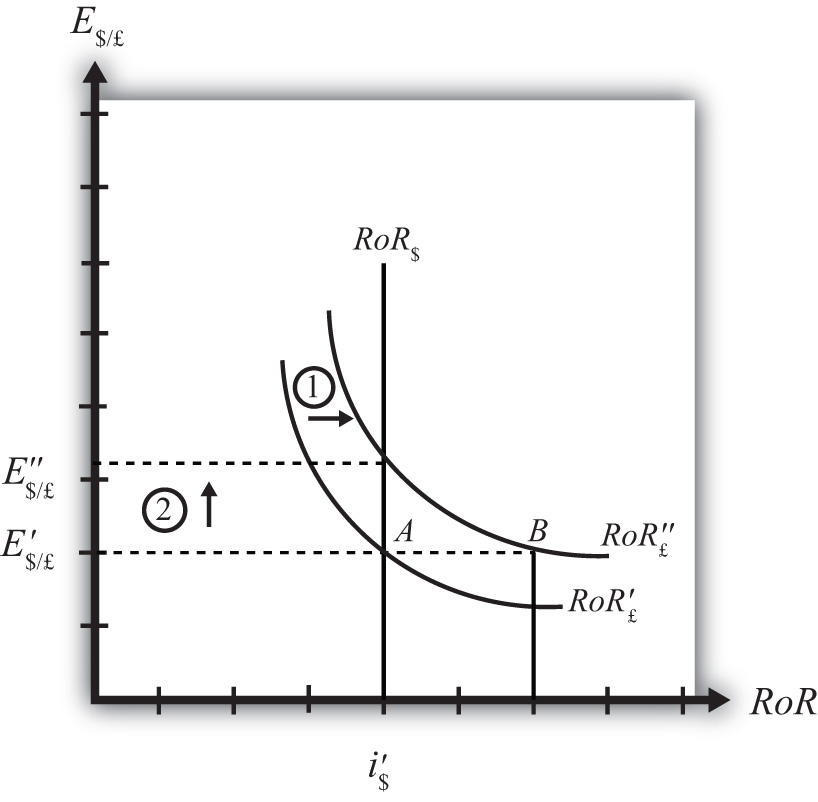
When a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial markets. There are opportunities for covered interest arbitrage. The Fisher effect states that. Interest Rate Parity IRP is best defined as. Interest rate parity IRP is the fundamental equation that governs the relationship between interest rates and currency exchange rates. When a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial markets. Interest Rate Parity IRP is best defined as. An arbitrage condition that must hold when international financial markets are in equilibrium. None of the options occurring when a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial markets.
The basic premise of interest rate parity is that hedged. When a government brings its domestic interest rate in line with other major financial marketsB. Covered interest rate parity refers to a theoretical condition in which the relationship between interest rates and the spot and forward currency values of two countries are in equilibrium. Interest Rate Parity IRP is best defined as O an arbitrage condition that must hold when international financial markets are in equilibrium. According to IRP theory the interest rate differential between two countries is equal to the differential between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange rate. There are opportunities for covered interest arbitrage. The basic premise of interest rate parity is that hedged.





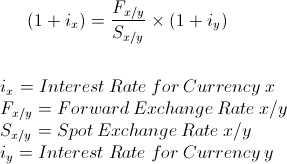
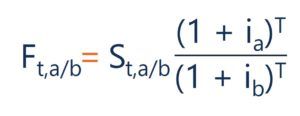











/forex2-5bfc2b91c9e77c00517fd323.jpg)















Post a Comment for "Interest Rate Parity (irp) Is Best Defined As"